1. Build the circuit shown below on a solderless board.
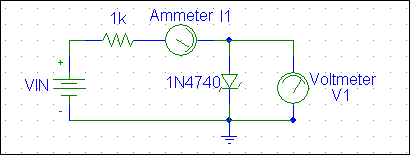
- Vary VIN between –12 V and +10 V in 0.5 V intervals. Measure I1 and V1. The voltmeter should be disconnected during the current measurements for VIN between -12 V and 0 V. Explain why you should disconnect the voltmeter as recommended. Would it affect your data?
- Plot a graph of V1 versus I1. On this graph, determine the breakdown voltage of the Zener diode.
- For VIN > 0, convert the measured currents to log10. Plot voltage on the independent axis and log10 (I1) on the dependent axis. From this graph determine the value of IS.
- Set VIN = 1 V. Place a soldering iron tip close to the diode without touching it. Observe what happens. Does this agree with the temperature characteristic of diodes? Explain.
2. Design problem.
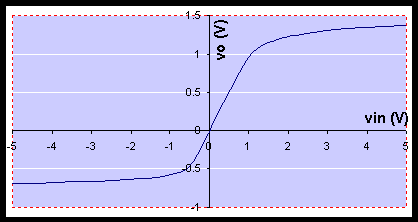
Design a circuit that has the characteristic of the graph shown. The maximum current in the circuit is about 50 mA. You are given diodes (1N4001), and you need to choose a resistor. Sketch vo versus time for vin = 10 sin (2pft). (f = 1 kHz)
Simulate the circuit you design using pSpice. Plot vo versus vin.
Build the circuit and vary vin between -5 V and 5 V, and measure vo. Measure at least 20 points. Use these points to plot vo versus vin.
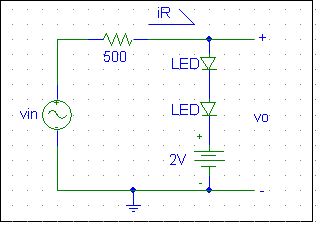
3. Build the circuit shown. Let vin be a triangular wave with a 20 Vp-p amplitude. Sketch vin and vo versus time. Change the 2 V source to –2 V. Sketch vo versus time. What happens when vin is less than the 2 V source? Explain.
4. Build the full-wave rectifier shown below. All the diodes are type 1N4001. R = 100 W, vin = 10 sin (2p ft), and f = 1 kHz.
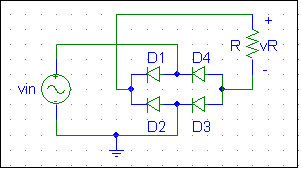
- Sketch the following signals versus time with respect to vin:
- vR
- vD2
- vD3
- Are the peak values of vin and vR equal? Explain.