1. Set up the circuit shown below on a solderless breadboard.
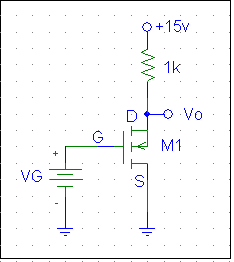
- Increase VG from 0 V to 5 V in step of 0.1 V, measure current ID and output voltage VO. Plot VGS vs. ID. Determine K and Vt.
- Adjust VG so that ID = 1 mA. Record VGS, VDS, and ID. Calculate gm.
- Add vg = 0.4 sin 2p ft with f = 1kHz in series with VG. Measure the small-signal output voltage on the oscilloscope and determine the voltage gain.
[K can be obtained using the PolyFit function in Matlab. Plot the polynomial using the constants you obtained and compare it with the plot from your data. K will be the second order constant when the two plots fit closely. Use the K found to calculate Vt. Verify your Vt from the transistor data book.]
2. Set up the circuit shown below on a solderless board.
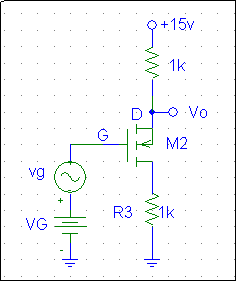
- With vg = 0 V, adjust VG so that ID = 1 mA. Record VGS, VDS, and ID.
- Let vg = 0.4 sin 2p ft with f = 1kHz. Calculate the ac input resistance rin.
- Calculate the ac output resistance r0 looking into the output voltage vo.
- Measure the small-signal output voltage on the oscilloscope and calculate the voltage gain.