1. Build a current mirror with two discrete npn transistors.
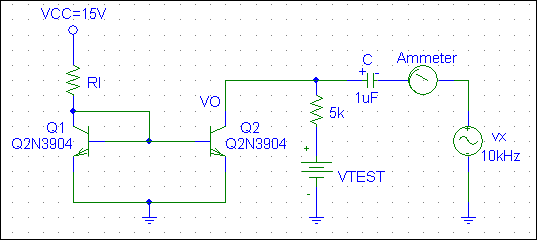
- Use two discrete npn transistors and measure the b for each transistor.
- Select RI so that II (or IRI) approximate 1 mA.
- Vary VTEST from 0 V to 10 V in 0.5 V increments. Record IO (or IC2) and VO (or VC2) for each value of VTEST. Plot Io/II versus VTEST. Over what range of the VTEST does the circuit function as a current mirror?
- Determine rout by measuring the collector-to-ground small-signal output resistance. This is done by ac-coupling an ac test voltage vx to the collector of Q2 and measuring the small-signal current ix. Notice that the resistance looking into the collector of Q2 is in parallel with the 10 kW resistor. Do this procedure for VTEST = 1 V, 5 V, and 10 V. Where could you move the ammeter so that this measurement is made directly? Which value of the current from the range should you take to calculate the small-signal output resistance?
2. Build the Widlar current mirror shown below.
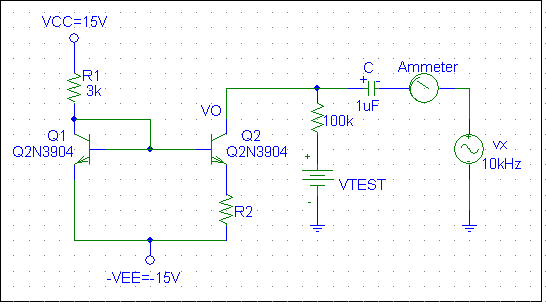
- Let RI = 3 kW . Adjust VCC so that II approximate 1 mA. Determine R2 so that IO approximate 40 m A.
- Vary VTEST from 0 V to 10 V in 1 V increments. Record IO and VC for each value of VTEST. Plot IO/II versus VTEST. Over what range of the VTEST does the circuit function as a current mirror?
- Use the same method as Part 1 and measure the small-signal resistance of the collector, rout. Remember, the resistance seen looking into the collector of Q2 is in parallel with the 100 kW resistor. You can move the ammeter to measure the current directly. Repeat this measurement for VTEST equal to 1 V, 5 V, and 10 V.