The measurement metrics for the AAL 5 include AAL 5 PDU interarrival times, AAL 5 PDU size, AAL 5 PDU error ratio, bit error ratio, and AAL 5 throughput. The PDU size measurement belongs to the traffic statistics collection category, while the rest of the metrics are for performance testing purposes.
Table ![]() summarizes the scenarios for performance testing in
the AAL 5.
summarizes the scenarios for performance testing in
the AAL 5.
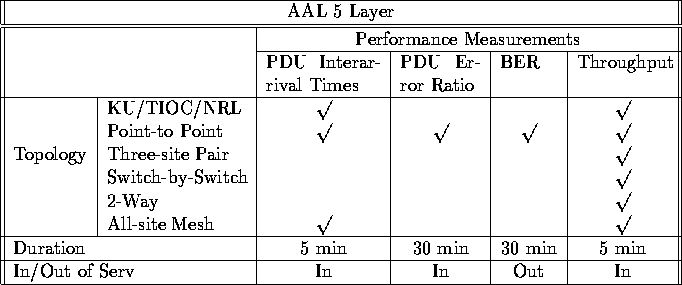
Table: AAL 5 Performance Testing Scenarios
Statistically, AAL 5 PDU size is topology-independent, so it will be measured using the KU/TIOC/NRL three-point configuration.
In the AAL 5, we define the PDU error ratio as:
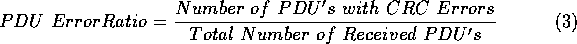
It is expected that the PDU error ratio is not dependent on measurement topology. For this reason, we chose to test this metric under the point-to-point configuration only.
The bit error ratio (BER) is not dependent on test topology. Instead, it depends heavily on the quality of the hardware that the testing bit stream traverses. For this reason, we chose to test the BER metric under the point-to-point configuration only. Also notice that the BER measurement can only be tested by using an out-of-service technique. The reason is that the ATM protocol does not support bit error checking at the cell level. A bit stream with a known pattern will be sent from the transmitter, and the receiver will test for bit errors by comparing the received bit pattern with the known pattern.
Distinct services allow for different ranges of BER. The RACE (Research on
Advanced Communication in Europe) consortium 1022 (Technology for ATM) considers bit
error ratios in the order of 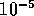 acceptable for remote process control
and hifi sound,
acceptable for remote process control
and hifi sound, 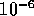 for broadcast video, and
for broadcast video, and 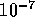 for data transmission
and telephony [4].
for data transmission
and telephony [4].
AAL 5 PDU interarrival (inter-transmission) times can be an indicator of AAL 5 PDU delay jitter (variation). If we know the timestamps for both the PDU departure and arrival events for the same AAL 5 PDU source, the delay variation can be evaluated even though the network clocks may not be synchronized. The way of estimating the AAL 5 PDU delay jitter is similar to that of the TCP layer packet delay variation estimation in the previous section.
The PDU interarrival times are expected to be dependent on the test topology. As the load on a particular link of the network is increased, we expect to see a higher variance on the PDU delay. Among our chosen topologies, the highest variance should occur for the All-Site Mesh Configuration.
Throughput performance will be tested under all topological configurations by using the ATMSTAT program. We expect the throughput performance to be dependent on the measurement topology. The ideal throughput should be close to the capacity of the network links in use for any given topology.