Traffic statistics and performance measurements
will be collected for the Application Layer.
To the measurements described in [2], we have added the throughput
of a given connection.
Table ![]() summarizes the scenarios in which the experiments will take place. These
scenarios include the topology of the test network, the duration of the
measurements, and whether they will be taken using in-service or out-of-service
techniques.
summarizes the scenarios in which the experiments will take place. These
scenarios include the topology of the test network, the duration of the
measurements, and whether they will be taken using in-service or out-of-service
techniques.
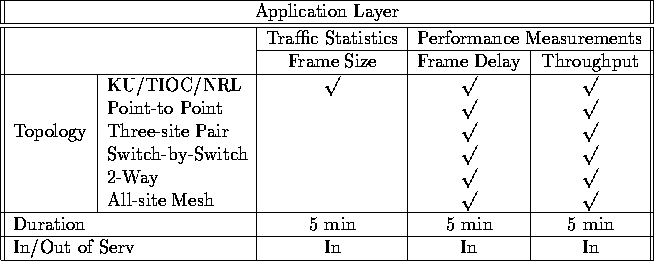
Table: Application Layer Scenarios
The applications which will be used for these experiments include:
As seen in Table ![]() , the experiment to determine the size of
a frame in bytes will only be performed for one of the configurations, since
the frame size is topology-independent.
, the experiment to determine the size of
a frame in bytes will only be performed for one of the configurations, since
the frame size is topology-independent.
On the other hand, the frame delay is expected to vary under different scenarios. As we increase the traffic competing for the same link, queueing effects will cause the frame delay to increase. In this fashion, supposing all other traffic in the network remains constant, we expect to measure the longest frame delay in the All-Site Mesh configuration and the shortest in the Point-to-Point configurations.
Since the AAI network must provide a wide variety of services, the frame delay must not exceed the highest acceptable delay for these services. The services which are most sensitive to end-to-end delay are telephony (transmission of speech) and distributed computing.
We expect to verify acceptable delays are achievable for the services which we will be testing (high-speed data transmission, image applications, etc.).
We can obtain the throughput of a given connection directly from NETSPEC. We will transmit data using NETSPEC under two conditions: constant bit rate (CBR) and full speed. The throughput should remain constant while the network experiences acceptable loads and decrease rapidly at the onset of congestion. Between each of the WAN Switches and the main sites there exists a DS3 connection; the bandwidth of these connections is in the order of 34 Mbps. Therefore, we expect to measure throughput to be close to 34 Mbps as long as the network is not congested.